

Main interface showing the synthetic data generator with all controls
### Generated Data Preview

Generated CSV preview with the Wine dataset reference
### Histogram plots

Example of Histogram comparison plot in the Wine dataset
### Boxplots

Example of Boxplot comparison
### Video Demo [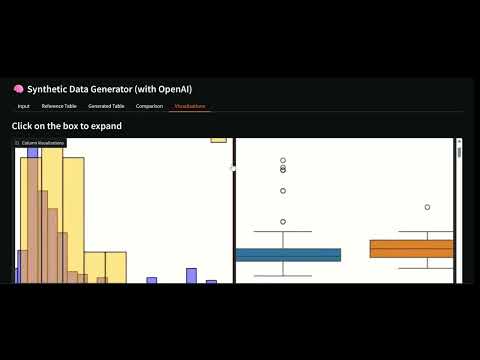](https://youtu.be/C7c8BbUGGBA) *Click to watch a complete walkthrough of the application* ## 📋 Features - **Intelligent Generation**: Generates synthetic data using OpenAI models (GPT-4o-mini, GPT-4.1-mini) - **Web Interface**: Provides an intuitive Gradio UI with real-time data preview - **Reference Data**: Optionally load CSV files to preserve statistical distributions - **Export Options**: Download generated datasets directly in CSV format - **Included Examples**: Comes with ready-to-use sample datasets for people and sentiment analysis - **Dynamic Batching**: Automatically adapts batch size based on prompt length and reference sample size - **Reference Sampling**: Uses random subsets of reference data to ensure variability and reduce API cost. The sample size (default `64`) can be modified in `src/constants.py` via `N_REFERENCE_ROWS`. ## 🚀 Installation ### Prerequisites - Python 3.12+ - OpenAI account with API key ### Option 1: Using pip ```bash # Create virtual environment python -m venv venv source venv/bin/activate # On Windows: venv\Scripts\activate # Install dependencies pip install -r requirements.txt ``` ### Option 2: Using uv ```bash # Clone the repository git clone https://github.com/Jsrodrigue/synthetic-data-creator.git cd synthetic-data-creator # Install dependencies uv sync # Activate virtual environment uv shell ``` ### Configuration 1. Copy the environment variables example file: ```bash cp .env_example .env ``` 2. Edit `.env` and add your OpenAI API key: ``` OPENAI_API_KEY=your_api_key_here ``` ## 🎯 Usage ### Start the application You can run the app either with **Python** or with **uv** (recommended if you installed dependencies using `uv sync`): ```bash # Option 1: using Python python app.py # Option 2: using uv (no need to activate venv manually) uv run app.py ``` The script will print a local URL (e.g., http://localhost:7860) — open that link in your browser. ### How to use the interface 1. **Configure Prompts**: - **System Prompt**: Uses the default rules defined in `src/constants.py` or can be edited there for custom generation. - **User Prompt**: Specifies what type of data to generate (default: 15 rows, defined in `src/constants.py`). 2. **Select Model**: - `gpt-4o-mini`: Faster and more economical - `gpt-4.1-mini`: Higher reasoning capacity 3. **Load Reference Data** (optional): - Upload a CSV file with similar data - Use included examples: `people_reference.csv`, `sentiment_reference.csv` or `wine_reference.csv` 4. **Generate Data**: - Click "🚀 Generate Data" - Review results in the gradio UI - Download the generated CSV ## 📊 Quality Evaluation ### Simple Evaluation System The project includes a simple evaluation system focused on basic metrics and visualizations: #### Features - **Simple Metrics**: Basic statistical comparisons and quality checks - **Integrated Visualizations**: Automatic generation of comparison plots in the app - **Easy to Understand**: Clear scores and simple reports - **Scale Invariant**: Works with datasets of different sizes - **Temporary Files**: Visualizations are generated in temp files and cleaned up automatically ## 🛠️ Improvements and Next Steps ### Immediate Improvements 1. **Advanced Validation**: - Implement specific validators by data type - Create evaluation reports 2. **Advanced Quality Metrics** - Include more advanced metrics to compare multivariate similarity (for future work), e.g.: - C2ST (Classifier Two‑Sample Test): train a classifier to distinguish real vs synthetic — report AUROC (ideal ≈ 0.5). - MMD (Maximum Mean Discrepancy): kernel-based multivariate distance. - Multivariate Wasserstein / Optimal Transport: joint-distribution distance (use POT). 3. **More Models**: - Integrate Hugging Face models - Support for local models (Ollama) - Comparison between different models ### Advanced Features 1. **Conditional Generation**: - Data based on specific conditions - Controlled outlier generation - Maintaining complex relationships 2. **Privacy Analysis**: - Differential privacy metrics - Sensitive data detection - Automatic anonymization 3. **Database Integration**: - Direct database connection - Massive data generation - Automatic synchronization ### Scalable Architecture 1. **REST API**: - Endpoints for integration - Authentication and rate limiting - OpenAPI documentation 2. **Asynchronous Processing**: - Work queues for long generations - Progress notifications - Robust error handling 3. **Monitoring and Logging**: - Usage and performance metrics - Detailed generation logs - Quality alerts ## 📁 Project Structure ``` synthetic_data/ ├── app.py # Main Gradio application for synthetic data generation ├── README.md # Project documentation ├── pyproject.toml # Project configuration ├── requirements.txt # Python dependencies ├── data/ # Reference CSV datasets used for generating synthetic data │ ├── people_reference.csv │ ├── sentiment_reference.csv │ └── wine_reference.csv ├── notebooks/ # Jupyter notebooks for experiments and development │ └── notebook.ipynb ├── src/ # Python source code │ ├── __init__.py ├── constants.py # Default constants, reference sample size, and default prompts │ ├── data_generation.py # Core functions for batch generation and evaluation │ ├── evaluator.py # Evaluation logic and metrics │ ├── IO_utils.py # Utilities for file management and temp directories │ ├── openai_utils.py # Wrappers for OpenAI API calls │ └── plot_utils.py # Functions to create visualizations from data └── temp_plots/ # Temporary folder for generated plot images (auto-cleaned) ``` ## 📄 License This project is under the MIT License. See the `LICENSE` file for more details. ## 🎓 Course Context & Learning Outcomes This project was developed as part of the [LLM Engineering: Master AI and Large Language Models](https://www.udemy.com/course/llm-engineering-master-ai-and-large-language-models/learn/lecture/52941433#questions/23828099) course on Udemy. It demonstrates practical implementation of: ### Key Learning Objectives: - **Prompt Engineering Mastery**: Creating effective system and user prompts for consistent outputs - **API Integration**: Working with OpenAI's API for production applications - **Data Processing**: Handling JSON parsing, validation, and error management - **Web Application Development**: Building user interfaces with Gradio ### Course Insights Applied: - **Why OpenAI over Open Source**: This project was developed as an alternative to open-source models due to consistency issues in prompt following with models like Llama 3.2. OpenAI provides more reliable and faster results for this specific task. - **Production Considerations**: Focus on error handling, output validation, and user experience - **Scalability Planning**: Architecture designed for future enhancements and integrations ### Related Course Topics: - Prompt engineering techniques - LLM API integration and optimization - Selection of best models for each usecase. --- **📚 Course Link**: [LLM Engineering: Master AI and Large Language Models](https://www.udemy.com/course/llm-engineering-master-ai-and-large-language-models/learn/lecture/52941433#questions/23828099)